User guide¶
The simplest use can be understood with an example. Suppose we want to calculate the power flow of the following system:
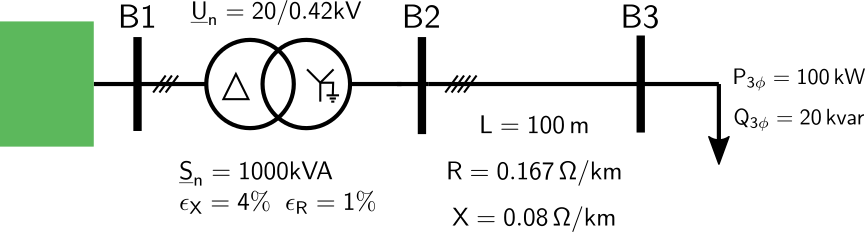
The following steps should be considered:
- Import modules
- Define or load grid parameters
- Generate a grid instance
- Read grid parameters
- Run power flow
- Post process results
- Plot results
Import modules¶
First of all, we have to import the relevant modules and classes:
import numpy as np
from pydgrid import grid
Define or write grid parameters¶
The network can be introduced in two ways:
- Python dictionary
- json file with the same structure as in the case of the previous python dictionary
For the proposed system example the following elemnts from pydgrid should be considered:
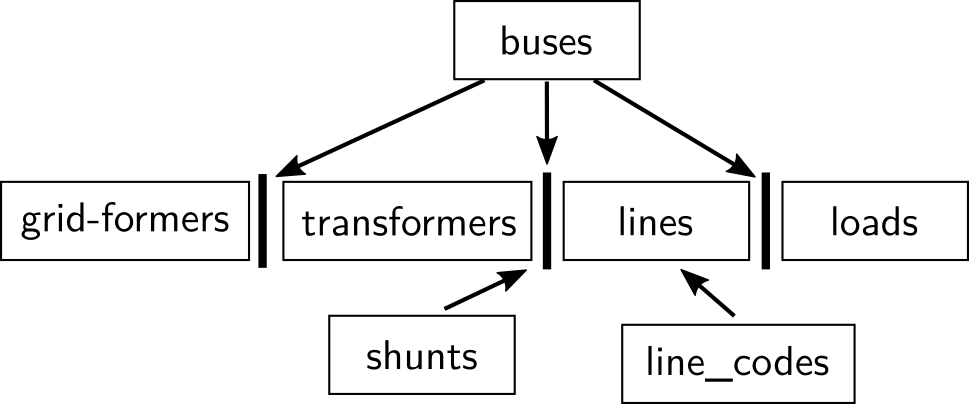
data = {
"buses":[
{"bus": "B1", "pos_x": 0, "pos_y": 0, "units": "m", "U_kV":20.0},
{"bus": "B2", "pos_x": 10, "pos_y": 0, "units": "m", "U_kV":0.4},
{"bus": "B3", "pos_x": 100, "pos_y": 0, "units": "m", "U_kV":0.4}
],
"grid_formers":[
{"bus": "B1",
"bus_nodes": [1, 2, 3], "deg": [0, -120, -240],
"kV": [11.547, 11.547, 11.547]}
],
"transformers":[
{"bus_j": "B1", "bus_k": "B2", "S_n_kVA": 1000.0, "U_j_kV":20, "U_k_kV":0.42,
"R_cc_pu": 0.01, "X_cc_pu":0.04, "connection": "Dyn11", "conductors_j": 3, "conductors_k": 4},
],
"lines":[
{"bus_j": "B2", "bus_k": "B3", "code": "lv_cu_150", "m": 100.0},
],
"loads":[
{"bus": "B3" , "kVA": 300.0, "pf": 0.85,"type":"3P+N"}
],
"shunts":[
{"bus": "B2" , "R": 0.001, "X": 0.0, "bus_nodes": [4,0]}
],
"line_codes":
{"lv_cu_150": {"Rph":0.167,"Xph":0.08, "Rn":0.167, "Xn": 0.08}
}
}
Generate a grid instance¶
grid_1 = grid()
Read grid parameters¶
grid_1.read(data)
Execute power flow¶
grid_1.pf()
Plot results¶
In the case of using jupyter notebook results can be visualized with a bokeh plot that includes hover tools.
from pydgrid.plot_bokeh import plot_results
plot_results(grid_1)
An on-line working jupyter notebook with the same example can be obtained here: